Top Questions about Helpful Links
-
Common Mistakes



"Mini" - Archivo creado con las dimensiones incorrectas. 
El archivo no tiene la resolución correcta para imprimir. Necesita ser 300 píxeles / pulgadas. 
Archivo de imágen tiene las dimensiones correctas. 
Archivo de la imágen está en la resolución apropiada para imprimir (300 píxeles / pulgada). 




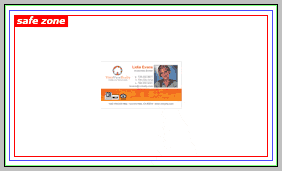
" Fuera de zona " - El texto está ubicado fuera del margen seguro. La información será cortada. 
Todo el texto y gráficos importantes están dentro del margen seguro. 




"Pixelated" - Text and / or images are not print ready hi-resolution. Your files must be in 300 pixels / inch resolution. We do not recommend using web images for print. 
File and images used are in proper print resolution specifications and will print correctly and clear. 




"Hard To Read" - Text created with conflicting colour values, no shadows on complex backgrouds, or very thin, tiny font will be very difficult to read. 
Text created with the proper contrasting colour and large font sizes will be very readable. 




"Borders" - We do not recommend borders due to the nature of our cutting. You will need to either remove the border, or put them well inside the safe zone. Do not place a border on the trim of bleed zone, it will be cut off or removed. 
Border, if desired, is placed well inside the safety zone. 




"Blank Card" - Created or uploaded card with no text, images, or any other information. 
All text and images were correctly created. 




"No Text" - Created or uploaded card with no text. 
All text information is present and correct. 




"Crop Marks" - Incorrectly placed or unnecessary crop marks will cause your image to upload incorrectly. 
Correctly used Crop Marks or removing them will allow file to be uploaded correctly for print. 




"Not Full Bleed" - Background is not fully extended to the edge. This will cause white strips to be around your card after it is cut. 
Background extends all the way to the edge on both sides. Card will be trimmed properly. -
Guidelines & Cutting Explained
At OvernightPrints we allow printing to the edge of the products and we take pride in having the tightest cutting margins available. These margins are 1,61mm and are named full-bleed. Trim Marks
The product will be cut on the trim mark (blue line), however the cut may shift up to 1,61mm in any direction.Full Bleed
If you wish to have coloured backgrounds or images continue to the edge of the product they must continue past the trim marks to the full bleed margin. If they do not continue to the full bleed margin you most likely will end up with white strips along the edge of the product due to cutting tolerance.Safe Zone
The text or other elements you want to guarantee not to be trimmed off must be placed within the safe zone. If they are placed directly next to the trim mark and the cutting is off but within tolerance, the text will be chopped off.
Note: If you choose the option rounded corners, you should make sure your image is 2-3 mm within the safety zone in order to prevent your image from getting cut during the processing of the corners.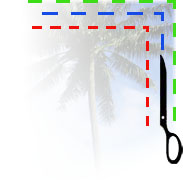
-
File Help
Design templates
Please choose one of the following possibilities to create your design:
-
RGB & CMYK
The two most common colour schemes are RGB and CMYK. An RGB colour scheme consists of three colours: Red, Green and Blue. These three colours are projections of light that can be overlapped in millions of colour-strengths and combinations to create on-screen colours and images. RGB colours are associated with television screens and computer monitors, but is not used in offset printing.
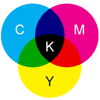
CMYKCMYK:
CMYK is made up of four colours: Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black. In full-colour process printing, CMYK is the standard method for offset printing. In the printing process, CMYK colours are measured by their subtractive/ reflective values; when the coloured ink is applied to paper, the surface of the paper reflects some colour and the non-reflective (that is, absorbent) colour is seen. CMYK colours are obtained by mixing the strengths of each colour to produce a new colour. The colours are mixed in percentages: 0% represents no colour, whereas 100% represents a maximum use of colour.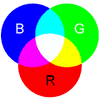
RGBRGB:
The RGB colour process and the CMYK colour process work in opposite ways. An RGB colour scheme forms colour through an additive process; to obtain white, all 3 colours are added together, and to obtain black, all 3 colours are removed. In contrast, the CMYK printing process obtains white by omitting all colour, and obtains black by using all four colours. One of the major benefits of RGB colour is its capacity to produce many more colours than CMYK can. Unfortunately, RGB colours cannot be correctly converted into CMYK. People often find that a colour, especially a neon colour, created in RGB can"t be converted correctly into CMYK but instead appears as an "out of gamut" colour, which is usually dark and "muddy." To spot these colour errors, and to prevent printing nightmares, it"s imperative that all files are uploaded in CMYK format before any printing occurs.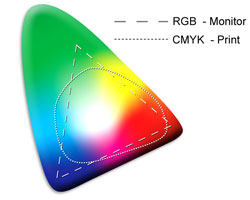 Color Spectrum:
Color Spectrum:
The CMYK process is not without its own drawbacks. One of the major difficulties of CMYK is its recognition of the colour blue. When blues are converted into CMYK, they have a tendency to print in purple. This is because blues are very closely related to purples in the CMYK colour scheme. To create a purple colour in CMYK, there are two variations of colour strengths: 80% cyan/90% magenta, and 100% cyan/100% magenta. To create a blue, very similar colour strengths are applied: 100% cyan/60% magenta. Because the creation of purple and the creation of blue are so similar, any small error that occurs while creating the document, taking it to pre-press, or printing it out, can change the colour from blue to purple. To prevent this colour change, we recommend that you reduce the amount of Magenta in your file to increase the likelihood that the colour will remain blue when printed.
CMYK also has difficulty with dark reds. When dark reds are converted and printed, they have a tendency to print as dark browns. Like blues and purples, dark reds and dark browns have similar colour percentages. Creating a dark red in CMYK requires 100% magenta/100% yellow/60% black. Creating a dark brown requires 70% magenta/100% yellow/80% black. To keep your dark reds from printing as dark browns, we recommend that you reduce the amount of Black in them.
-
Glossary
CMYK: Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black. In full-colour process printing, CMYK is the standard method for offset printing. CMYK colours are measured by their subtractive/reflective values; when the coloured ink is applied to paper, the surface of the paper reflects some colour and the non-reflective (that is, absorbent) colour is seen. more »
RGB: Red, Green and Blue. These three colours are projections of light that can be overlapped in millions of colour-strengths and combinations to create on-screen colours and images. RGB colours are associated with television screens and computer monitors, but is not used in offset printing. more »
RGB & CMYK: The RGB colour process and the CMYK colour process work in opposite ways. An RGB colour scheme forms colour through an additive process; to obtain white, all 3 colours are added together, and to obtain black, all 3 colours are removed. In contrast, the CMYK printing process obtains white by omitting all colour, and obtains black by using all four colours. more »
Full Bleed: A small amount of size added to all four sides of a file to ensure the background is printed and cut to fill up the entire card as opposed to seeing a white thin line going around the edge of the card. Usually the added file size is either 1,61mm or 3,175mm.
Colour Match: A colour will never print out to exactly to match its on-screen source. Colours vary from monitor to monitor, and different printers produce different colour results. All these variables affect the printed outcome.
Pleasing Colour: Colour that when printed is close enough to the original colour requested without becoming an entirely new colour.
Cutting Tolerance: The margin of error that a cutting machine has to cut paper. It can be 1/16 inch or 1/8 inch. This means the trim line that it is suppose to cut down can vary up to either 1,61mm or 3,175mm depending on the cutting tolerance for the order.
Colour Drift: This occurs when a colour shifts away from its original value and becomes a new colour. It becomes a gradient in a way, it starts with the original colour then blends into a new colour at the end.
Incorrect Colour Selection: This is when you select a colour that doesn't exist in the colour gamut (the available colours in a certain colour mode) you are using. In CMYK there are colours that don't exist within the CMYK colour gamut but exist in another colour gamut such as RGB. They are referred to as “out of gamut” colours. Out of gamut colours can be seen when they are either viewed in CMYK mode or in the final output when they are printed. Often a new or altered colour is seen.
Crop Marks: A pair of thin lines that are at each corner of a file that show where the file ends.
Card Orientation: There are two types of orientation, vertical ( up and down) and horizontal (left to right).
U/V Coating: Standard printing process used. The process consist of a plate that makes an inked impression on a rubber-blanketed cylinder which in turn transfers it to the paper. This is the printing process used by all major printing companies as well as newspaper and magazine printers.




